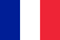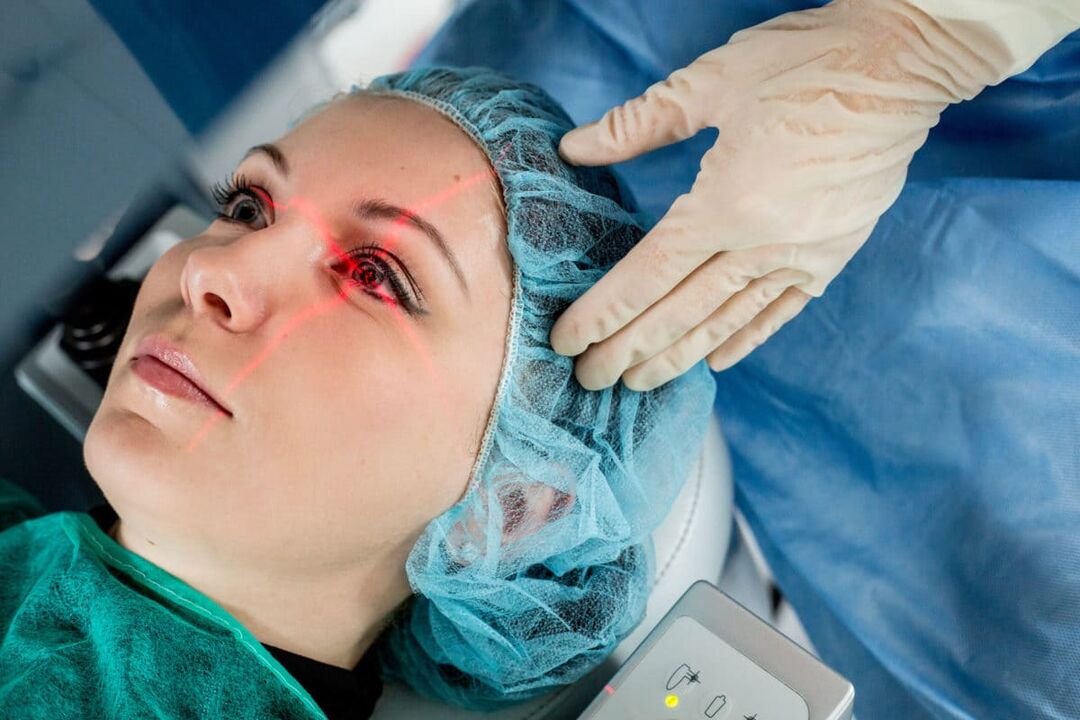
What is laser vision correction and when is it performed?
- Myopia (nearsightedness). In this condition, people have trouble focusing on distant objects because the light in front of the retina is overfocused. Laser vision correction reshapes the cornea to focus light on the retina, improving distance vision.
- Hyperopia (farsightedness). A condition in which a person has difficulty seeing close objects clearly, usually due to refractive problems. This procedure corrects the disease in just 1 surgery.
- astigmatism. A vision disorder in which the cornea or lens of the eye is asymmetrical or irregularly shaped. This causes a distortion in the focusing of light on the retina of the eye, resulting in blurred and distorted images at both near and far distances.
When is laser vision correction recommended?
- Intolerant of contact optics. If a patient has difficulty wearing contact lenses or causes various problems, including discomfort, allergic reactions, or corneal damage, laser correction may be recommended as an alternative method of correcting vision.
- Type of occupation or activity. There are many professions that require good vision but don't wear glasses or contacts - pilots, military personnel, athletes or firefighters. Laser correction may be recommended to improve vision and ensure independence from corrective aids.
- Myopia (from -1 to -15 diopters), hyperopia (from +3 diopters) and astigmatism (up to +5 diopters). Corrective surgery can improve near vision and eliminate the need to wear glasses or contact lenses for near work.
Type of vision correction surgery performed
- LASIK (assisted in situ keratomileusis). In one of the most common laser vision correction procedures, the surgeon creates a thin flap-like peel on the cornea, then lifts it to reveal the depth of the correction, and uses a laser to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue. The valve is then reinstalled into place, ensuring quick healing and minimal pain.
- PRK (photorefractive keratectomy). Another surgical option to restore vision clarity is to completely remove the surface layer of the cornea and apply a laser directly to the exposed surface. After surgery, the cornea will heal on its own, but it will take some time for vision to return.
Contraindications for laser vision correction
- Still young. Laser vision correction is not recommended for children and teenagers because their eyes are still developing.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding. A woman's vision may change during this period, so it is recommended to postpone surgery until breastfeeding is over.
- Refractive changes. Laser correction is not recommended for patients with significant changes in clarity due to conditions such as diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma.
- Physical damage to the cornea. If the patient has scars, ulcers, or other corneal irregularities, laser correction may not be an appropriate or safe procedure.
- Dry eyes. Patients who frequently experience burning sensation in their eyes may experience worsening of symptoms after laser vision correction treatment.
- Corneal disease. Laser vision correction is not recommended for patients with conditions such as keratoconus or corneal dystrophy.
- There is something wrong with the eyes. Patients with certain fundus diseases, including macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy, may have surgical limitations.
- Autoimmune diseases. People with autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or Sjogren's syndrome) may be at increased risk for complications after laser surgery.
- Eye infection or inflammation. If there is an active eye infection, inflammatory process, or conjunctivitis, it is recommended to postpone laser correction until complete recovery.
- taking certain medications. Some medications that affect the immune system can also affect the healing process after laser correction, so their use may be contraindicated.
How Laser Vision Correction Works: The Surgery Phase
- Initial inspection. Before surgery, patients must undergo an initial eye examination, which includes measuring visual acuity, checking the shape and thickness of the cornea, and the general condition of the eye.
- anaesthetization. Before the surgery begins, the patient's eyes will be sedated with anesthesia.
- Create a corneal flap. The surgeon uses a mechanical or laser device to create a small flap in the cornea. To create the valve, a microkeratome method or a femtosecond laser can be used.
- Vision Correction. After creating the corneal flap, doctors use an excimer laser to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue. This changes its shape to correct vision errors. In the case of myopia, the center of the cornea becomes flatter, while in the case of hyperopia, the center of the cornea becomes steeper. To correct astigmatism, the shape of the cornea changes accordingly.
- Close the valve. After vision correction is complete, the surgeon carefully closes the created corneal flap. It is usually self-fixing and requires no sutures.
Benefits of Laser Vision Correction
- High efficiency. Laser vision correction is one of the most successful vision correction methods available today because the procedure can significantly improve people's vision.
- Recovery is fast. Most patients experience very rapid vision recovery after laser correction. Within a few days after surgery, they can resume daily activities and even resume driving.
- Eliminates the inconvenience caused by contact lenses and glasses. The surgery eliminates the need for glasses, which is especially convenient for people who play sports or have an active lifestyle.
- The duration for which results are obtained. In most cases, the results of laser vision correction are stable and long-lasting. After surgery, many patients have stable vision, and some do not even require additional correction.
- Personalized treatment from a reliable clinic. Modern laser vision correction technology allows for highly personalized surgery. Doctors use advanced equipment to create accurate corneal maps and analyze other factors that are appropriate for each patient. This allows for the highest precision and results best suited to each individual's needs.
- Convenient and comfortable. After laser vision correction, patients no longer need to worry about wearing glasses or contact lenses. This brings great convenience and comfort to daily life.
- Corrections are extensive. Laser vision correction can be used to correct various types of refractive errors, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. This means that most people with these vision problems can have this surgery.
- fast. Laser vision correction itself usually only takes a few minutes per eye. This is a very quick process, allowing patients to quickly get the results they want and return to their normal activities.
- The risk of complications is low. Modern laser vision correction surgery carries a lower risk of complications. Thanks to advances in technology and physician experience, complications are less likely to occur and most patients experience safe, successful results.